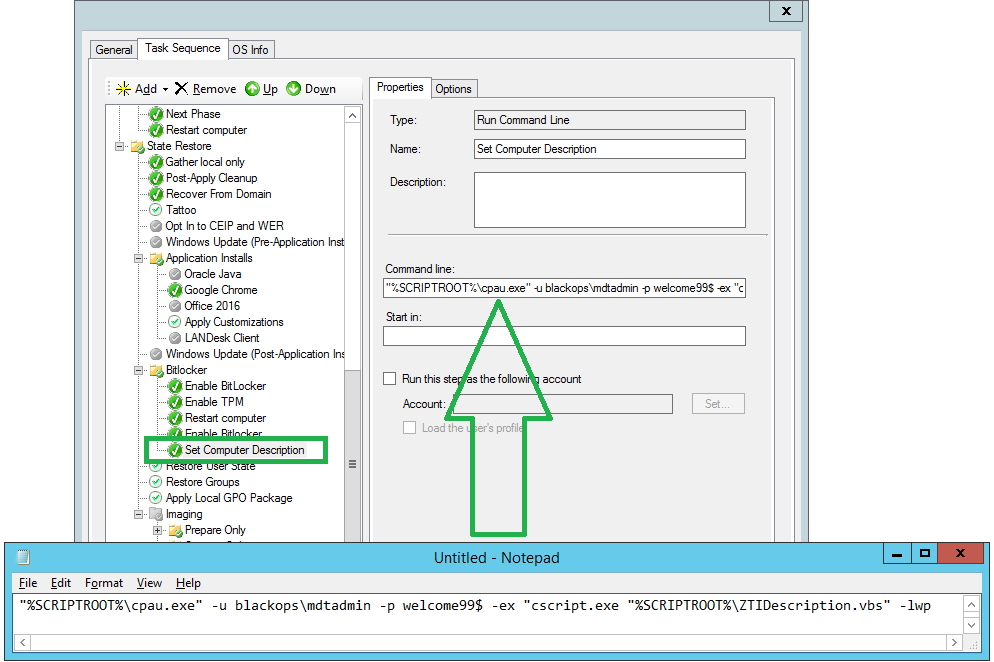
I created this to write Active Directory user properties to the registry, which would then been queried by desktop management software for reporting purposes.
This does have built-in site detection, so you may or may not need that. For me, I needed to determine a user’s site using a range of IP’s from a text file, as well as query FIM data from AD.
ON ERROR RESUME NEXT
CONST ForReading = 1
DIM Line_Input, StartIP_Input, EndIP_in, StartIP, PerfServIP, PrefServName, IPRange, OctetIncrement
DIM OctetCompare, IP_Address, objFSO, objFile, objOutput, workingData, IsMatchFound, ws, SiteName
DIM RegCommand1, RegCommand2, RegCommand3, RegCommand4, RegCommand5, RegCommand6
DIM RegCommand7, RegCommand8, RegCommand9
SET objShell = CreateObject("Wscript.Shell")
'SETS CURRENT DIRECTORY TO VARIABLE
strCurrentDirectory = objShell.CurrentDirectory
IsMatchFound = 0'set to False by default
SET objFSO = createobject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
'List containing IP ranges and site names
'example from text file: 11.80.00.1,11.80.40.254,11.80.40.60,MyFileServerName,Florida.
SET objFile = objFSO.openTextFile(strCurrentDirectory & "\AllSiteList.txt", ForReading)
'used for testing
'example of output: Texas
SET objOutput = objFSO.CreateTextFile(strCurrentDirectory & "\site.txt")
workingData = ""
'RETURN IP ADDRESS USING A FUNCTION
IP_Address = ReturnIPAddress()
'RETURN SITE LOCATION
DO UNTIL objFile.atEndOfStream
'READ LINE FROM FILE
workingData = objFile.readLine & vbCrLf
'SPLIT THE LINE INTO AN ARRAY
Line_Input = Split(workingData, ",")
'SPLIT THE STARTING IP INTO IT'S BASE OCTETS
StartIP_Input = Split(Line_Input(0), ".")
'SPLIT THE ENDING IP RANGE INTO IT'S BASE OCTETS
EndIP_in = Split(Line_Input(1), ".")
'USES THE STARTIP STRING AS THE FIRST OF TWO COMPARISONS TO FIND A MATCHING IP WITHIN THE RANGE
StartIP = StartIP_Input(0) & "." & StartIP_Input(1) & "." & StartIP_Input(2)
'PLACES SITE INFORMATION INTO VARIABLE
SiteName = LINE_INPUT(4)''''add the site location name
'CALCULATE THE NUMBER OF IP SUBNETS WE NEED TO INCREMENT THROUGH TO CHECK THE RANGE
IPRange = CINT(EndIP_in(2)) - CINT(StartIP_Input(2))
'INITIALIZE THE INCREMENT
OctetIncrement = CINT(StartIP_Input(2))
'COMPARE IP OCTETS WITH IP RANGES (YOU COULD ADD GATEWAYS AS WELL)
FOR i = 0 TO IPRange
IF InStr(IP_Address, StartIP) > 0 THEN
OctetCompare = Split(IP_Address, ".")
IF CINT(OctetCompare(2)) = OctetIncrement THEN
IsMatchFound = 1'found match
'objOutput.Write SiteName'writes to file
'msgbox SiteName'displays in message box
RegCommand1 = "reg add hkcu\MYINFO /v SiteLocation /t REG_SZ /d " & SiteName & " /f /reg:64"
objOutput.Close
OctetIncrement = IPRange
i = IPRange
EXIT DO
END IF
END IF
'if not found, increment until found
OctetIncrement = OctetIncrement + 1
StartIP = StartIP_Input(0) & "." & StartIP_Input(1) & "." & CSTR(OctetIncrement)
NEXT
LOOP
objFile.Close
DIM objSysInfo,objUser,objShell,strUser
SET objSysInfo = CreateObject("ADSystemInfo")
'RETURN CURRENT USER
strUser = objSysInfo.UserName
'CREATE AD USER OBJECT
SET objUser = GetObject("LDAP://" & strUser)
'IMPORT PROPERTIES INTO REG KEYS
'Location
objShell.Run RegCommand1,0,true'applies reg key
'Display Name
RegCommand2 = "reg add hkcu\MYINFO /v DisplayName /t REG_SZ /d " & chr(34) & objUser.displayName & chr(34) & " /f /reg:64"
objShell.Run RegCommand2,0,true'applies reg key
'SAM Account Name
RegCommand3 = "reg add hkcu\MYINFO /v AccountName /t REG_SZ /d " & chr(34) & objUser.sAMAccountName & chr(34) & " /f /reg:64"
objShell.Run RegCommand3,0,true'applies reg key
'Business Unit
RegCommand4 = "reg add hkcu\MYINFO /v BusinessUnit /t REG_SZ /d " & objUser.fimwpoBusinessUnit & " /f /reg:64"
objShell.Run RegCommand4,0,true'applies reg key
'Business Unit Description
RegCommand5 = "reg add hkcu\MYINFO /v BusinessUnitDescription /t REG_SZ /d " & chr(34) & objUser.fimwpoBusinessUnitDescription & chr(34) & " /f /reg:64"
objShell.Run RegCommand5,0,true'applies reg key
'Business Title
RegCommand6 = "reg add hkcu\MYINFO /v BusinessTitle /t REG_SZ /d " & chr(34) & objUser.fimwpoBusinessTitle & chr(34) & " /f /reg:64"
objShell.Run RegCommand6,0,true'applies reg key
'User email address
RegCommand7 = "reg add hkcu\MYINFO /v EmailAddress /t REG_SZ /d " & chr(34) & objUser.mail & chr(34) & " /f /reg:64"
objShell.Run RegCommand7,0,true'applies reg key
'Employee ID
RegCommand8 = "reg add hkcu\MYINFO /v EmployeeID /t REG_SZ /d " & chr(34) & objUser.employeeID & chr(34) & " /f /reg:64"
objShell.Run RegCommand8,0,true'applies reg key
'Department
RegCommand9 = "reg add hkcu\MYINFO /v Department /t REG_SZ /d " & chr(34) & objUser.department & chr(34) & " /f /reg:64"
objShell.Run RegCommand9,0,true'applies reg key
'IP FUNCTION - WILL RETURN CURRENT IP ADDRESS
FUNCTION ReturnIPAddress()
DIM ws : SET ws = CreateObject("WScript.Shell")
DIM fso : SET fso = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
DIM tempFile : tempFile = fso.GetSpecialFolder(2) & "/ip.txt"
DIM LineFromOutput, IP
IF ws.Environment("SYSTEM")("OS") = "" Then
ws.run "winipcfg /batch " & tempFile, 0, True
ELSE
ws.run "%comspec% /c ipconfig > " & tempFile, 0, True
END IF
WITH fso.GetFile(tempFile).OpenAsTextStream
DO WHILE NOT .AtEndOfStream
LineFromOutput = .ReadLine
IF InStr(LineFromOutput, "Address") <> 0 Then IP = Mid(LineFromOutput, InStr(LineFromOutput, ":") + 2)
Loop
.Close
End WITH
IF IP <> "" Then
IF Asc(Right(IP, 1)) = 13 Then IP = Left(IP, Len(IP) - 1)
END IF
ReturnIPAddress = IP
fso.GetFile(tempFile).Delete
SET fso = Nothing
SET ws = Nothing
End Function
Could be used for LANDesk, SCCM, or other desktop management software to read the stored values in the registry.