This is a work in progress, but I have created a program to elevate a specified application. The idea is, you need to run an application under a restricted user profile, but cannot because it requires admin privileges—this gets around that. The program also bypasses UAC! Written in C#. I use the SecureString, ProcessStartInfo, and MemoryStream classes to do exactly what I needed—securely elevate an application. Originally written for Windows 7 (back in 2014) to only elevate executable files, but I’m adding support for Windows 10 and scripting languages as well.
Current Features
--Accepts executables
--Accepts batch files
--Accepts any passed parameters for program
--Accepts an AES string for password
--Accepts an encrypted reg key for password
--Option to wait for program to exit
--Create tighter try/catches (done 04/11/2017)
--Remove second console window on batch files (done 04/14/2017)
--Create more methods from existing code (done 04/11/2017)
--Add logging in registry (done 11/29/2017)
--Add logging in event log (done 11/29/2017)
--Add VBScript support (done 12/15/2017)
Future Ideas
--Add a required pin number for internal script use
--Add domain support
AES Information
AES has three fixed 128-bit block ciphers with cryptographic key sizes of 128, 192 and 256 bits. Key size is unlimited, whereas the block size maximum is 256 bits. The AES design is based on a substitution-permutation network (SPN) and does not use the Data Encryption Standard (DES) Feistel network.
In 1997, the NIST initiated a five-year algorithm development process to replace DES and Triple DES. The NIST algorithm selection process facilitated open collaboration and communication and included a close review of 15 candidates. After an intense evaluation, the Rijndael design, created by two Belgian cryptographers, was the final choice.
AES replaced DES with new and updated features:
- Block encryption implementation
- 128-bit group encryption with 128, 192 and 256-bit key lengths
- Symmetric algorithm requiring only one encryption and decryption key
- Data security for 20-30 years
- Worldwide access
- No royalties
- Easy overall implementation
How doe AES work?

What does the diagram mean?
• AES is a block cipher with a block length of 128 bits.
• AES allows for three different key lengths: 128, 192, or 256 bits.
• Encryption consists of 10 rounds of processing for 128-bit keys, 12 rounds for 192-bit keys, and 14 rounds for 256-bit keys.
• Except for the last round in each case, all other rounds are identical.
• Each round of processing includes one single-byte based substitution step, a row-wise permutation step, a column-wise mixing.
• To appreciate the processing steps used in a single round, it is best to think of a 128-bit block as consisting of a 4 × 4 matrix of bytes, arranged as follows:
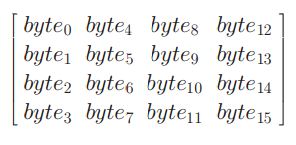
• Therefore, the first four bytes of a 128-bit input block occupy the first column in the 4 × 4 matrix of bytes. The next four bytes occupy the second column, and so on. more on AES…
Screenshot of Jump tool in action

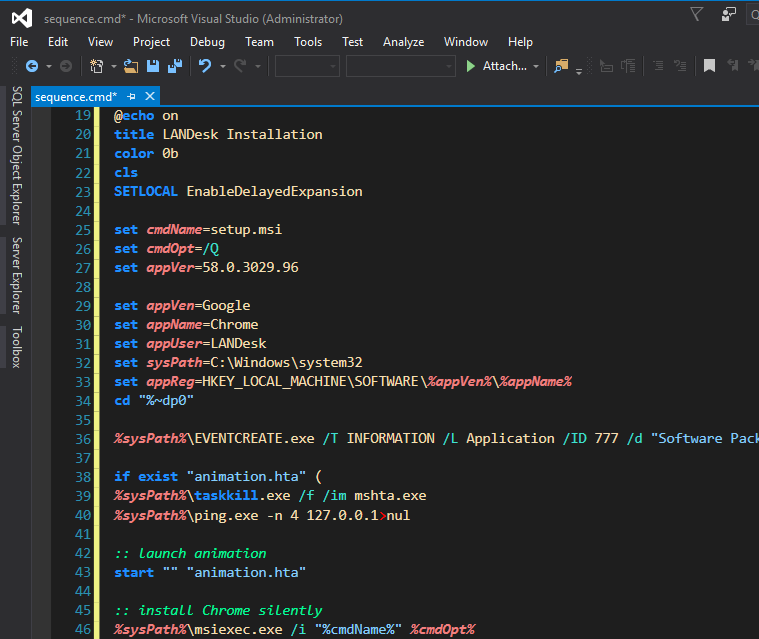
Screenshot of elevation working

The Code (click to view source code)
using System;
using System.IO; // used by MemoryStream
using System.Diagnostics; // used by Process
using System.Linq; // used by ToArray
using System.Security; // used by SecureString
using System.Text; // used by Encoding
using System.Security.Cryptography; // used by aes
using Microsoft.Win32; // used by registry
using System.Collections.Generic; // used by List (quotes)
using System.Text.RegularExpressions;
namespace Jump
{
class JumpUtil
{
//////////////////////////////////////////////////
// See all class declarations at the bottom
//////////////////////////////////////////////////
//////////////////////////////////////////////////
// See notes at the bottom
//////////////////////////////////////////////////
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// CONSOLE HEADER
//----------------------------------------------------
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Cyan;
Console.WriteLine("\nJump v1.0.0.1 December 2017");
Console.WriteLine("\nLaunch Windows-based applications in elevated mode");
Console.WriteLine("\nEddie Jackson | mrnettek@gmail.com | eddiejackson.net");
Console.WriteLine("\nUsage: -app \"notepad.exe\" -opt \"name.txt\" -secure \"rEqnfiteGwLsktuW==\" -wait\n");
// QUOTE
// returns the random quote
SubQuote();
// BEGIN
// load items into array
// this loads arguments from the command line into an array
foreach (string s in args)
{
for (int i = 0; i < args.Length; i++)
{
array = args[i].ToString();
}
// contains contents of array
arrayString = arrayString + s.ToString() + " ";
}
// END - LOAD ITEMS INTO ARRAY
// SPACES
// initialized to detect spaces and assign variables accordingly
// regex wasn't working properly when I added spaces
string inputstring = arrayString.ToString();
string[] inputstringarray = inputstring.Split(' ');
// APP
// does the command line contain the -app parameter?
if (arrayString.Contains(parameterApp))
{
// found the -app parameter
returnIndex = Array.IndexOf(inputstringarray, parameterApp);
returnedApp = args[returnIndex + 1];
//returnedApp = FindNextValue(arrayString, parameterApp); // regex doesn't work right. Disabled for now.
if (returnedApp != parameterSecure &&
returnedApp != parameterOpt &&
returnedApp != parameterWait &&
returnedApp != "")
{
appName = returnedApp;
}
}
else
{
// the -app parameter is completely missing
Messenger(Message1);
Environment.Exit(6);
}
// OPTION
// does the command line contain the -opt parameter?
// I use string[] and IndexOf to read spaces in the options parameter
// regex wasn't working properly when I added spaces
if (arrayString.Contains("-opt"))
{
// found the -opt parameter
returnIndex = Array.IndexOf(inputstringarray, parameterOpt);
// return what follows the -opt parameter
returnedOpt = args[returnIndex + 1];
// accommodate extra spaces in file name - useful for vbs files
if (returnedOpt == parameterSecure) {
returnedOpt = args[returnIndex + 0];
}
// make sure returnedOpt isn't the AES variable
if (returnedOpt.Contains("=="))
{
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Red;
Console.Write("\n\nMissing data from the -opt parameter!\n");
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Gray;
Environment.Exit(6);
}
// validate return option meets conditions
if (
returnedOpt != parameterSecure &&
returnedOpt != parameterApp &&
returnedOpt != parameterWait &&
returnedOpt != "")
{
// set options
appOpt = returnedOpt;
}
else {
// check for data following -opt parameter
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Red;
Console.Write("\n\nMissing data from the -opt parameter!\n");
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Gray;
Environment.Exit(6);
}
}
// SECURE
// does the command line contain the -secure parameter?
if (arrayString.Contains(parameterSecure))
{
// found the -secure parameter
returnedSecure = FindNextValue(arrayString, parameterSecure);
if (returnedSecure != parameterApp &&
returnedSecure != parameterOpt &&
returnedSecure != parameterWait &&
returnedSecure != "")
{
appPassword = (Decrypt(returnedSecure.ToString()));
}
else {
// check for data following -secure parameter
Messenger(Message2);
Environment.Exit(6);
}
}
else
{
// the -secure parameter is completely missing
Messenger(Message6);
Environment.Exit(6);
}
// WAIT
// does command line contain the -wait parameter?
if (arrayString.Contains(parameterWait))
{
// found the -wait parameter
appWait = "True";
}
else
{
// did not find the -wait parameter
appWait = "False";
}
// DETERMINE FILE TYPE
// mostly made for handling batch files
// had no issues with EXEs
//----------------------------------------------------
string retVBS = "FALSE";
string retBAT = "FALSE";
string extension = Path.GetExtension(appName);
if (extension.ToLower() == ".cmd") { retBAT = "TRUE"; }
if (extension.ToLower() == ".bat") { retBAT = "TRUE"; }
if (extension.ToLower() == ".vbs") { retVBS = "TRUE"; }
// BEGIN - ELEVATED APP LAUNCH
// use SecureString
//----------------------------------------------------
SecureString securePassword = new SecureString();
Array.ForEach(appPassword.ToArray(), securePassword.AppendChar);
securePassword.MakeReadOnly();
// instantiate process from Process
Process process = new Process();
ProcessStartInfo startInfo = new ProcessStartInfo
{
// set up default properties
UserName = appUser,
Domain = "",
Password = securePassword,
LoadUserProfile = true,
UseShellExecute = false,
CreateNoWindow = true,
RedirectStandardOutput = true,
RedirectStandardError = true
};
// CMD, BAT
// IF A BATCH FILE, DO THIS
// the reason I created this was because there is
// an EXTRA black window when launching batch files
// using SecureString :: quite annoying MS hasn't
// done something about this
//----------------------------------------------------
if (retBAT == "TRUE")
{
try
{
// DOES THE FILE EXIST???
if (!File.Exists(appName))
{
Messenger(Message10);
Environment.Exit(4);
}
startInfo.FileName = @"C:\Windows\SysWOW64\Wscript.exe";
startInfo.Arguments = "_hide.vbs";
string path = "_hide.vbs";
string text0 = "On error resume next:";
File.WriteAllText(path, text0);
// builds the vbscript
using (StreamWriter sw = File.AppendText(path))
{
string text1 = "";
string text2 = "";
if (appOpt != "")
{
// with option
text1 = "Set WshShell = CreateObject(\"WScript.Shell\"):";
text2 = "WshShell.Run chr(34) & " + "\"" + appName + "\"" + " & chr(34) & \" \" & chr(34) & " + "\"" + appOpt + "\"" + " & chr(34)" + ",0, true";
}
else {
// without option
text1 = "Set WshShell = CreateObject(\"WScript.Shell\"):";
text2 = "WshShell.Run chr(34) & " + "\"" + appName + "\"" + " & chr(34)" + ",0, true";
}
// writes the vbs to file
sw.WriteLine(text1);
sw.WriteLine(text2);
}
// instantiates the process
process = Process.Start(startInfo);
// checks to see if -wait is true
if (appWait == "True") { process.WaitForExit(); }
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Green;
Console.WriteLine("\nGreat Success!\n");
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.White;
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(1000);
// if this gets lost, I'll probably just add a %temp% path
if (File.Exists("_hide.vbs"))
{
File.Delete("_hide.vbs");
}
Audit();
Environment.Exit(0);
}
catch (Exception)
{
Messenger(Message8);
}
}
// VBS
// IF A VBSCRIPT FILE, DO THIS
//----------------------------------------------------
if (retVBS == "TRUE")
{
try
{
// DOES THE FILE EXIST???
if (!File.Exists(appName))
{
Messenger(Message10);
Environment.Exit(4);
}
startInfo.FileName = @"C:\Windows\SysWOW64\Wscript.exe";
if (appOpt != "")
{
//startInfo.Arguments = appName + " " + "\"" + appOpt + "\"";
startInfo.Arguments = "\"" + appName + "\"" + " " + "\"" + appOpt + "\"";
process = Process.Start(startInfo);
}
else
{
startInfo.Arguments = "\"" + appName + "\"";
process = Process.Start(startInfo);
}
if (appWait == "True") { process.WaitForExit(); }
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Green;
Console.WriteLine("\nGreat Success!\n");
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.White;
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(1000);
Audit();
Environment.Exit(0);
}
catch (Exception)
{
Messenger(Message8);
}
}
// EXE
// IF AN EXECUTABLE FILE, DO THIS
//----------------------------------------------------
// does app exist?
try
{
// I have added a little bit of extra logic for EXEs, specifically 'system' EXEs that may be in Windows or System32 folders
// I append the .EXE and relative system paths just as an extra feature to find 'known' EXEs. Otherwise, EXEs like ping,
// calc, notepad, net, reg, etc., would fail without the path being explicitly defined
if (!File.Exists(appName) && (!File.Exists(appName + ".exe")))
{
if (!File.Exists("C:\\Windows\\" + appName + ".exe") && (!File.Exists("C:\\Windows\\" + appName)))
{
if (!File.Exists("C:\\Windows\\system32\\" + appName + ".exe") && (!File.Exists("C:\\Windows\\system32\\" + appName)))
{
Messenger(Message10);
Environment.Exit(4);
}
}
}
startInfo.FileName = appName;
if (appOpt != "") { startInfo.Arguments = "\"" + appOpt + "\""; }
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow;
Console.WriteLine("Elevating...");
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.White;
process = Process.Start(startInfo);
if (appWait == "True") { process.WaitForExit(); }
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Green;
Console.WriteLine("\nGreat Success!\n");
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.White;
Audit();
Environment.Exit(0);
}
catch (Exception)
{
Messenger(Message8);
}
}
// END - ELEVATED APP LAUNCH
// RETURN NEXT VALUE
public static string FindNextValue(string inputArray, string inputSearch)
{
sNext = "";
if (arrayString.Contains(inputSearch))
{
string[] sRegX = Regex.Split(inputArray, @"[^’a-zA-Z0-9\\\:\=\-\._]+");
int index = Array.IndexOf(sRegX, inputSearch);
if (index < sRegX.Count() - 1)
sNext = sRegX[index + 1];
}
return sNext;
}
// BASIC LOGGING
static void Audit()
{
// create registry key
string reg1 = "HKEY_CURRENT_USER";
string reg2 = @"SOFTWARE\Jump\";
string regPath = reg1 + @"\" + reg2;
string UName = System.Security.Principal.WindowsIdentity.GetCurrent().Name;
string regVal = appName + " " + UName;
DateTime dt = DateTime.Now;
Registry.SetValue(regPath, dt.ToString(), regVal, RegistryValueKind.String);
// log event
string sSource;
string sLog;
string sEvent;
sSource = "Jump.exe";
sLog = "Application";
sEvent = appName + " was installed using the Jump tool by " + UName;
if (!EventLog.SourceExists(sSource)) EventLog.CreateEventSource(sSource, sLog);
EventLog.WriteEntry(sSource, sEvent);
// output to console
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.White;
Console.WriteLine("{{{ Security log has been updated }}}\n");
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Gray;
}
// Just show header of jump util
static void Help()
{
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.White;
Environment.Exit(0);
}
// import and show message
static void Messenger(string message)
{
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Red;
Console.WriteLine("\n{0}\n", message);
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.White;
Environment.Exit(2);
}
// returns random quote
static void SubQuote()
{
QuoteGenerator quoteGenerator = new QuoteGenerator();
string retQuote = quoteGenerator.ReturnRandomQuote();
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Gray;
Console.WriteLine("{0}\n", retQuote);
Console.WriteLine("");
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.White;
}
// decoding
public static string Decrypt(string strData)
{
try
{
if ((strData.Length % 4) == 0)
{
//aes string length is good
return Encoding.UTF8.GetString(Decrypt(Convert.FromBase64String(strData)));
}
Messenger(Message9);
Environment.Exit(6);
return null;
}
catch (Exception)
{
Messenger(Message9);
Environment.Exit(6);
return null; // prevents return error message
}
}
// decrypt
public static byte[] Decrypt(byte[] strData)
{
try
{
PasswordDeriveBytes passbytes =
new PasswordDeriveBytes(strPermutation,
new byte[] { bytePermutation1,
bytePermutation2,
bytePermutation3,
bytePermutation4
//Reference: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.security.cryptography.passwordderivebytes%28v=vs.110%29.aspx?f=255&MSPPError=-2147217396
});
MemoryStream memstream = new MemoryStream();
Aes aes = new AesManaged();
aes.Key = passbytes.GetBytes(aes.KeySize / 8);
aes.IV = passbytes.GetBytes(aes.BlockSize / 8);
//Reference: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.security.cryptography.aesmanaged(v=vs.110).aspx
CryptoStream cryptostream = new CryptoStream(memstream,
aes.CreateDecryptor(), CryptoStreamMode.Write);
cryptostream.Write(strData, 0, strData.Length);
cryptostream.Close();
return memstream.ToArray();
//Reference: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.security.cryptography.cryptostream(v=vs.110).aspx
}
catch (Exception)
{
Messenger(Message8);
Environment.Exit(6); // exits in case the password fails
//return strData;
return null; // prevents return error message
}
}
class QuoteGenerator
{
Random random = new Random();
List<string> Quotes = new List<string>();
public QuoteGenerator()
{
Quotes.Add("Intelligence is the ability to adapt to change - Stephen Hawking");
Quotes.Add("Nothing endures but change - Heraclitus");
Quotes.Add("Dream big and dare to fail - Normal Vaughan");
Quotes.Add("If it doesn’t challenge you, it won’t change you - Fred DeVito");
Quotes.Add("Genius is talent set on fire by courage Henry Van Dyke");
Quotes.Add("Energy and persistence conquer all things - Benjamin Franklin");
Quotes.Add("The secret of getting ahead is getting started - Mark Twain");
Quotes.Add("The measure of who we are is what we do with what we have - Vince Lombardi");
Quotes.Add("With self-discipline most anything is possible - Theodore Roosevelt");
Quotes.Add("The price of greatness is responsibility - Winston Churchill");
Quotes.Add("Action is the foundational key to all success - Picasso");
Quotes.Add("Try not to become a man of success, but rather a man of value - Albert Einstein");
Quotes.Add("Learning never exhausts the mind - Leonardo da Vinci");
}
public string ReturnRandomQuote()
{
int quoteCount = Quotes.Count;
int randomNumber = random.Next(0, (quoteCount - 1));
return Quotes[randomNumber];
}
}
// the admin user account name
public const string appUser = "Administrator";
// use these permutations - change these
public const string strPermutation = "eqyshqfqhjk";
public const int bytePermutation1 = 0x11;
public const int bytePermutation2 = 0x19;
public const int bytePermutation3 = 0x17;
public const int bytePermutation4 = 0x11;
public const string strRegHive = "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE";
public const string strRegKey = @"SOFTWARE\Serial\";
public const string strRegPath = strRegHive + @"\" + strRegKey;
public const string strRegVal = "Serial1";
// general console messages
public const string Message1 = "Slow down there, Skippy. Did you forget the -app parameter?";
public const string Message2 = "Ohhh, man...did you forget to add the AES string?";
public const string Message3 = "Yo, where is the -opt parameter? Use -opt.";
public const string Message4 = "Wait a minute. Looks like -wait is missing.";
public const string Message5 = "Hey, dude, you forgot to enter an app name.";
public const string Message6 = "Houston, we have a problem. Did you forget to add the -secure parameter?";
public const string Message7 = "Too much, man...too much. You have too much in the command line.";
public const string Message8 = "Hold on, Chief. This isn't good...the app wasn't elevated.";
public const string Message9 = "Come on man...the AES string is too short.";
public const string Message10 = "The file seems to have taken a vacation. It can't be found!";
// the array, working space
public static string array = "";
// the items in the array
public static string arrayString = "";
// appVar(i) becomes appName, appOpt, appWait, appPassword
public static string appPassword = "";
public static string appName = "";
public static string appOpt = "";
public static string appWait = "";
private static string sNext;
public static string parameterApp = "-app";
public static string parameterWait = "-wait";
public static string parameterOpt = "-opt";
public static string parameterSecure = "-secure";
public static string returnedApp = "";
public static string returnedSecure = "";
public static string returnedOpt = "";
public static int returnIndex;
}
}
/*NOTES
SPACES IN THE DECRYPT STRING
64-bit encoding does not work well with spaces in the string for some odd reason.
Add the following: stringToDecrypt = stringToDecrypt.Replace(" ","+");
before this line "int len = stringToDecrypt.Length; inputByteArray = Convert.FromBase64String(stringToDecrypt);"
to replace blank spaces with '+'. Plus sign will be interpreted as a space when you call the FromBase64String method.
EXTRA BLACK WINDOW (CONSOLE WINDOW)
When using SecureString, and passing a username and password to a BATCH file process, an EXTRA black window appears.
The window is tied to the batch file :-( , and from what I can tell, cannot be so easily hidden. Yes, you can hide the main
process window, but not the child window. If you close the child window, it kills the batch file. Arrrrrg.
I was able to create a workaround using VBS output and hiding the batch process, but I will be looking for a better solution.
*/
Screenshot of Visual Studio (click to zoom)

* no longer uses a password – I’m passing in an AES string
Fun Fact
It would take a supercomputer 1 billion billion years to crack the 128-bit AES key using brute force attack. This is more than the age of the universe (13.75 billion years).