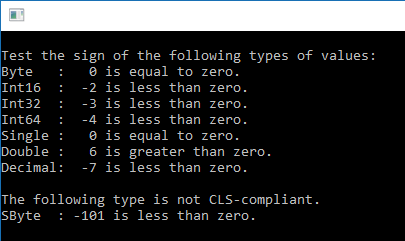
using System;
class Sample
{
public static void Main()
{
string str = "{0}: {1,3} is {2} zero.";
string nl = Environment.NewLine;
byte xByte1 = 0;
short xShort1 = -2;
int xInt1 = -3;
long xLong1 = -4;
float xSingle1 = 0.0f;
double xDouble1 = 6.0;
Decimal xDecimal1 = -7m;
// The following type is not CLS-compliant.
sbyte xSbyte1 = -101;
Console.WriteLine("{0}Test the sign of the following types of values:", nl);
Console.WriteLine(str, "Byte ", xByte1, Test(Math.Sign(xByte1)));
Console.WriteLine(str, "Int16 ", xShort1, Test(Math.Sign(xShort1)));
Console.WriteLine(str, "Int32 ", xInt1, Test(Math.Sign(xInt1)));
Console.WriteLine(str, "Int64 ", xLong1, Test(Math.Sign(xLong1)));
Console.WriteLine(str, "Single ", xSingle1, Test(Math.Sign(xSingle1)));
Console.WriteLine(str, "Double ", xDouble1, Test(Math.Sign(xDouble1)));
Console.WriteLine(str, "Decimal", xDecimal1, Test(Math.Sign(xDecimal1)));
//
Console.WriteLine("{0}The following type is not CLS-compliant.", nl);
Console.WriteLine(str, "SByte ", xSbyte1, Test(Math.Sign(xSbyte1)));
Console.Read();
}
//
public static String Test(int compare)
{
if (compare == 0)
return "equal to";
else if (compare < 0)
return "less than";
else
return "greater than";
}
}
Output