#include "stdafx.h" #include<iostream> using namespace std; int main(void) { float Fahrenheit, Celsius; cout << "Enter temperature in Celsius: "; cin >> Celsius; Fahrenheit = (Celsius * 9.0) / 5.0 + 32; cout << "The temperature in Celsius: " << Celsius << endl; cout << "The temperature in Fahrenheit: " << Fahrenheit << endl; getchar(); getchar(); }
Output
Month: January 2019
Python – User Input and Basic Logic
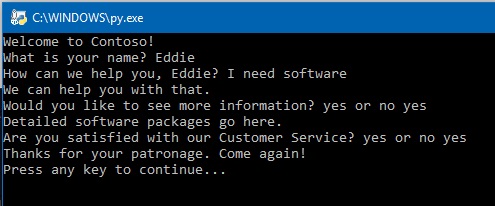
print("Welcome to Contoso!")
a = input("What is your name? ")
b = input("How can we help you, " + a +'? ')
print("We can help you with that.")
c = input("Would you like to see more information? yes or no ")
no = ("Come again!")
yes = ("Detailed software packages go here.")
if c=='yes' :
print(yes)
d = input ("Are you satisfied with our Customer Service? yes or no ")
if d=='yes':
print('Thanks for your patronage. Come again!')
else:
e = input('What can we help you with? ')
f = input("Press any key to continue...")
# add more logic here
Output
Notes
C# – Getter Setter Example
Getters and Setters are the accessors for the public property Name. You would use them to get/set the value of that property in an instance of Genre. That is an Auto-Implemented Property. It’s basically a shorthand way of creating properties for a class in C#, without having to define private variables for them.
using System;
class Program
{
// entry point
static void Main()
{
AccessClass accessClass = new AccessClass
{
// comment-uncomment to test get set
// our declared values
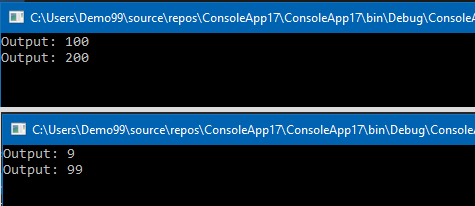
//Number1 = 9, // setter value
//Number2 = 99 // setter value
};
Console.WriteLine("Output: {0}", accessClass.Number1); // getter
Console.WriteLine("Output: {0}", accessClass.Number2); // getter
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
public class AccessClass
{
// our default values
public int _number1 { get; set; } = 100; // our default value, aka Backing store
public int _number2 { get; set; } = 200; // our default value, aka Backing store
public int Number1
{
get
{
return _number1;
}
set
{
_number1 = value;
}
}
public int Number2
{
get
{
return _number2;
}
set
{
_number2 = value;
}
}
}
Output
Notes