Clear-Host Write-Host "Output to file..." Get-ItemProperty HKLM:\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall\* | Select-Object DisplayName, DisplayVersion | Sort-Object DisplayName | Out-File -Encoding Ascii -append output.txt Get-ItemProperty HKLM:\SOFTWARE\WOW6432Node\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall\* | Select-Object DisplayName, DisplayVersion | Sort-Object DisplayName | Out-File -Encoding Ascii -append output.txt Get-WMIObject -Query "SELECT * FROM Win32_Product" | Select-Object Name, Version | Sort-Object Name, Version | Out-File -Encoding Ascii -append output.txt # or output just the app names #Get-WMIObject -Query "SELECT * FROM Win32_Product" | Select-Object -ExpandProperty Name | sort | Out-File -Encoding Ascii -append output.txt Write-Host "Output to screen..." Get-ItemProperty HKLM:\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall\* | Select-Object DisplayName, DisplayVersion | Sort-Object DisplayName Get-ItemProperty HKLM:\SOFTWARE\WOW6432Node\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall\* | Select-Object DisplayName, DisplayVersion | Sort-Object DisplayName Get-WMIObject -Query "SELECT * FROM Win32_Product" | Select-Object Name, Version | Sort-Object Name, Version notepad.exe output.txt Write-Host "" Write-Host "Done!" Write-Host ""
Month: December 2017
PowerShell – Disable UAC
Clear-Host
$numVersion = (Get-CimInstance Win32_OperatingSystem).Version
$numSplit = $numVersion.split(".")[0]
if ($numSplit -eq 10) {
Set-ItemProperty "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System" -Name "ConsentPromptBehaviorAdmin" -Value "0"
} ElseIf ($numSplit -eq 6) {
$enumSplit = $numSplit.split(".")[1]
if ($enumSplit -eq 1 -or $enumSplit -eq 0) {
Set-ItemProperty "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System" -Name "EnableLUA" -Value "0"
} Else {
Set-ItemProperty "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System" -Name "ConsentPromptBehaviorAdmin" -Value "0"
}
} ElseIf ($numSplit -eq 5) {
Set-ItemProperty "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System" -Name "EnableLUA" -Value "0"
} Else {
Set-ItemProperty "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System" -Name "ConsentPromptBehaviorAdmin" -Value "0"
}
Write-Host "Done!"
Write-Host ""
Windows 10 – Disable Background Apps
Add this to a login script or post setup script
REG Add HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\BackgroundAccessApplications /v GlobalUserDisabled /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f
see SuperFetch, which also needs to be disabled.
Windows 10 – Set Time and Time Zone Automatically
If you’re experiencing clock drift or incorrect time issues, try changing the time settings.
These are the registry keys for setting automatic time and time zones.
Time
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\W32Time\Parameters]
“Type”=”NTP”
Time Zone
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\tzautoupdate]
“Start”=dword:00000003
Notes
Set time from command line
admin cmd > tzutil /s “Eastern Standard Time”
Basic Clock Troubleshooting
Check auto assign time, Settings > Time and language
Check auto assign time zone, Settings > Time and language
Check service Windows Time, Services.msc > Windows Time
Check Date/Time server, Control Panel > Date and Time > Internet Time > Change Settings
Check the BIOS battery
net stop w32time
regsvr32 w32time.dll
w32tm /unregister
w32tm /register
net start w32time
w32tm /resync
sfc /scannow
Windows – Enable/Disable Superfetch
What is Superfetch?
To make it easier to understand, Superfetch is a service that helps to decrease boot time and make must-load programs more efficiently.
Let’s take an example and you can see for yourself how does Superfetch work exactly. Picture this: you just boot your PC. Then you double-click one of your Word documents. It takes about 5 seconds to open. Then you double-click another Word document, this time, it takes just about 2 seconds.
You see, Superfetch pre-loads certain apps based on your usage patterns, and the pre-load files are stored in your RAM. In doing so, you’re able to open your programs or apps so much faster and thus with better user experience.
…or so Microsoft claims.
As mentioned, you may find that Superfetch takes up much of your CPU usage and makes your PC slow to use. Read on and see what you should about it.
Should I Disable or Enable Superfetch?
Well, before you move on to disable or enable your Superfetch service, you should know that there is no hard proof whether Superfetch service would increase your PC performance in general.
If you open and close certain apps or programs a lot then you should leave Superfetch enabled. If Superfetch service takes up too much of your CPU or Memory usage to the point where it significantly slow down your PC, then you should definitely disable it.
You should also know that Superfetch service is fairly easy to disable or enable. You may need to test both options to know for sure what to do.
To modify whether Superfetch is enabled or disabled, you can perform the following steps:
Disable from Services
- Hold the Windows Key, while pressing “R” to bring up the Run dialog box.
- Type services.msc, then press Enter.
- The Services window displays. Find Superfetch in the list.
- Right-click Superfetch, then select Properties.
- Select the Stop button if you wish to stop the service. In the Startup type dropdown menu, choose Disabled.
Enable or Disable from Registry
- Using the Registry Editor, navigate to the following location.
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE
- SYSTEM
- CurrentControlSet
- Control
- Session Manager
- Memory Management
- PrefetchParameters
- On the right side, double-click on EnableSuperfetch. If this value doesn’t exist, right-click the PrefetchParameters folder, then choose New > DWORD Value.
- Give EnableSuperfetch one of the following values:
- 0 – to disable Superfetch
- 1 – to enable prefetching when program is launched
- 2 – to enable boot prefetching
- 3 – to enable prefetching of everything
- Select OK.
- Close the Registry Editor.
Also see disabling background apps
Notes
The full reg path
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Memory Management\PrefetchParameters
Windows – Remotely Install App and Mask Password
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 |
@echo off Cls Title Remote Installer 1.0 SetLocal EnableExtensions EnableDelayedExpansion cd "%~dp0" Set /p user=User: Set /P "=Password: " < Nul Call :PW set /p machine=Machine name: Echo. copy /y D:\tools\go.cmd \\%machine%\c$\Windows\system32\go.cmd copy /y D:\tools\setup.msi \\%machine%\c$\setup\setup.msi psexec.exe \\%machine% -u %user% -p !Mask! -i go.cmd Pause exit /b 0 :PW For /F skip^=1^ delims^=^ eol^= %%# in ( '"Echo(|Replace.exe "%~f0" . /U /W"') Do Set "Input=%%#" For /F %%# In ( '"Prompt $H &For %%_ In (_) Do Rem"') Do Set "Back=%%#" Set "Mask=" :_PW_KB Set "Char=" & For /F skip^=1^ delims^=^ eol^= %%# in ( 'Replace.exe "%~f0" . /U /W') Do Set "Char=%%#" If !Char!==!Input! Echo(&Goto :Eof If !Char!==!Back! (If Defined Mask (Set /P "=!Back! !Back!" <Nul Set "Mask=!Mask:~0,-1!" ) ) Else (Set /P "=*" <Nul If !Char!==! (Set "Mask=!Mask!^!" ) Else Set "Mask=!Mask!!Char!" ) Goto :_PW_KB |
Windows 10 – Open Reg Key at Specific Location
@echo off
:: check for input
if %1==”” exit /b 1
set REGKEY=%1
:: set reg key
REG ADD “HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Applets\Regedit” /v “LastKey” /d “%REGKEY%” /f
:: open registry editor
taskkill /f /im regedit.exe
start “” regedit.exe
Command
OpenLastKey.cmd HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion
Output
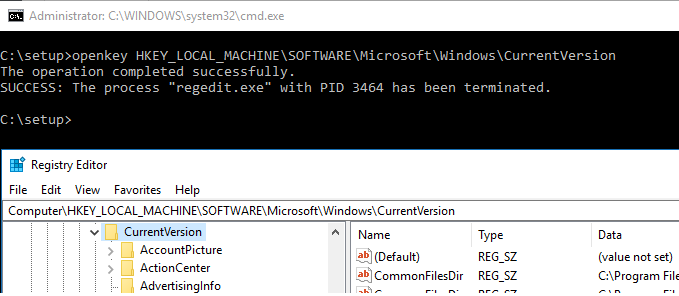
Notes
AutoHotKey Submitted by Rick Corbett
#j::
{
LK_loc = HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Applets\Regedit ; Location of LastKey entry
ClipSaved := ClipboardAll ; Save the current clipboard contents
Clipboard = ; Empty the clipboard
SendInput, ^c ; Copy selected registry key to the clipboard
ClipWait ; Wait for the clipboard to contain text
; Search and replace any abbreviations
StringReplace, Clipboard, Clipboard, HKCR, HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT
StringReplace, Clipboard, Clipboard, HKCC, HKEY_CURRENT_CONFIG
StringReplace, Clipboard, Clipboard, HKCU, HKEY_CURRENT_USER
StringReplace, Clipboard, Clipboard, HKLM, HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE
StringReplace, Clipboard, Clipboard, HKU, HKEY_USERS
RegWrite, REG_SZ, %LK_loc%, LastKey, %Clipboard% ; Write LastKey data from clipboard to registry as a string
Clipboard = ; Empty the clipboard
Clipboard := ClipSaved ; Restore the original clipboard contents
Run, %windir%\regedit.exe ; Open the Registry Editor
Return
}
Windows 10 – Repair System Files
Use dism to repair system files, restore configs, and fix OS anomalies.
Repair a Windows Image
If a Windows image becomes unserviceable, you can use the Deployment Imaging and Servicing Management (DISM) tool to update the files and correct the problem. You can use DISM to repair an offline Windows image in a WIM or VHD file, or an online Windows image. An online Windows image will also attempt to repair itself if it becomes unserviceable. The repair source for this operation is the same source that is used for Features on Demand and is determined by Group Policy settings. For more information, see Configure a Windows Repair Source. When you use the DISM tool to repair an online or offline image, you can use the /Source argument with the /RestoreHealth argument to specify additional repair source locations to use to search for the required files.
The DISM /ScanHealth, /CheckHealth, and /RestoreHealth arguments can only be used when servicing Windows.
To check if an image is repairable
Scan the image to check for corruption. This operation will take several minutes. At a command prompt, type the following command:
Dism /Online /Cleanup-Image /ScanHealth
Check the image to see whether any corruption has been detected. At a command prompt, type:
Dism /Online /Cleanup-Image /CheckHealth
When you use the /CheckHealth argument, the DISM tool will report whether the image is healthy, repairable, or non-repairable. If the image is non-repairable, you should discard the image and start again. If the image is repairable, you can use the /RestoreHealth argument to repair the image.
To repair an image
Use the /RestoreHealth argument to repair the image. To repair an offline image using a mounted image as a repair source, at a command prompt, type the following command:
Dism /Image:C:\offline /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth /Source:c:\test\mount\windows
Or to repair an online image using some of your own sources instead of Windows Update, type:
Dism /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth /Source:c:\test\mount\windows /LimitAccess
Notes
You can also use the older command:
sfc /scannow
Windows 10 – Fix Default Associations
Prevent Windows 10 from hijacking your application/file associations.
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
;——————-
;Microsoft.3DBuilder
;——————-
;File Types: .stl, .3mf, .obj, .wrl, .ply, .fbx, .3ds, .dae, .dxf, .bmp
;… .jpg, .png, .tga
[HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Classes\AppXvhc4p7vz4b485xfp46hhk3fq3grkdgjg]
“NoOpenWith”=””
“NoStaticDefaultVerb”=””
;——————-
;Microsoft Edge
;——————-
;File Types: .htm, .html
[HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Classes\AppX4hxtad77fbk3jkkeerkrm0ze94wjf3s9]
“NoOpenWith”=””
“NoStaticDefaultVerb”=””
;File Types: .pdf
[HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Classes\AppXd4nrz8ff68srnhf9t5a8sbjyar1cr723]
“NoOpenWith”=””
“NoStaticDefaultVerb”=””
;File Types: .svg
[HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Classes\AppXde74bfzw9j31bzhcvsrxsyjnhhbq66cs]
“NoOpenWith”=””
“NoStaticDefaultVerb”=””
;File Types: .xml
[HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Classes\AppXcc58vyzkbjbs4ky0mxrmxf8278rk9b3t]
“NoOpenWith”=””
“NoStaticDefaultVerb”=””
;——————-
;Microsoft Photos
;——————-
;File Types: .3g2,.3gp, .3gp2, .3gpp, .asf, .avi, .m2t, .m2ts, .m4v, .mkv
;… .mov, .mp4, mp4v, .mts, .tif, .tiff, .wmv
[HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Classes\AppXk0g4vb8gvt7b93tg50ybcy892pge6jmt]
“NoOpenWith”=””
“NoStaticDefaultVerb”=””
;File Types: Most Image File Types
[HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Classes\AppX43hnxtbyyps62jhe9sqpdzxn1790zetc]
“NoOpenWith”=””
“NoStaticDefaultVerb”=””
;File Types: .raw, .rwl, .rw2 and others
[HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Classes\AppX9rkaq77s0jzh1tyccadx9ghba15r6t3h]
“NoOpenWith”=””
“NoStaticDefaultVerb”=””
;——————-
; Zune Music
;——————-
;File Types: .aac, .adt, .adts ,.amr, .flac, .m3u, .m4a, .m4r, .mp3, .mpa
;.. .wav, .wma, .wpl, .zpl
[HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Classes\AppXqj98qxeaynz6dv4459ayz6bnqxbyaqcs]
“NoOpenWith”=””
“NoStaticDefaultVerb”=””
;——————-
; Zune Video
;——————-
;File Types: .3g2,.3gp, .3gpp, .avi, .divx, .m2t, .m2ts, .m4v, .mkv, .mod
;… .mov, .mp4, mp4v, .mpe, .mpeg, .mpg, .mpv2, .mts, .tod, .ts
;… .tts, .wm, .wmv, .xvid
[HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Classes\AppX6eg8h5sxqq90pv53845wmnbewywdqq5h]
“NoOpenWith”=””
“NoStaticDefaultVerb”=””
Notes
Program |
File Type(s) |
Key |
|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Edge | .htm, .html .svg .xml |
AppX4hxtad77fbk3jkkeerkrm0ze94wjf3s9 AppXd4nrz8ff68srnhf9t5a8sbjyar1cr723 AppXde74bfzw9j31bzhcvsrxsyjnhhbq66cs AppXcc58vyzkbjbs4ky0mxrmxf8278rk9b3t |
| Microsoft Photos | .asf, .tiff, and others Most image types .raw, .rwl, and others |
AppXk0g4vb8gvt7b93tg50ybcy892pge6jmt AppX43hnxtbyyps62jhe9sqpdzxn1790zetc AppX9rkaq77s0jzh1tyccadx9ghba15r6t3h |
| Groove Music | .mp3, .wav, .wma and others | AppXqj98qxeaynz6dv4459ayz6bnqxbyaqcs |
| Movies & TV | .avi, .mov, .mp4, and others | AppX6eg8h5sxqq90pv53845wmnbewywdqq5h |
SCCM – PowerShell – Remove Reg Keys on Remote Computers
I wrote this to remove GPRequestedSiteAssignmentCode and AssignedSiteCode registry values under the HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\SMS\Mobile Client registry key. Just add the computer names into the computers.txt file and run. Note, WINRM will need to be enabled on the remote computers/servers.
Clear-Host
$user = Read-Host "Enter Domain\Username"
$credential = Get-Credential -Credential "$user"
$Computers = Get-Content "c:\PowerShell\computers.txt"
try
{
Invoke-Command -ComputerName $Computers -Credential $credential -ScriptBlock {Remove-ItemProperty -Path HKLM:"\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\SMS\Mobile Client" -name AssignedSiteCode}
Invoke-Command -ComputerName $Computers -Credential $credential -ScriptBlock {Remove-ItemProperty -Path HKLM:"\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\SMS\Mobile Client" -name GPRequestedSiteAssignmentCode}
}
catch
{
$output = $_
$output
}
Windows – Fix Boot Issues
Common boot issues can be fixed by doing the following:
Method 1
Using a Windows boot disc, go to Startup Repair (do this 3-4 times, if necessary).
Method 2
If that doesn’t work try the Repair Option and this time choose Command Prompt, type:
BOOTREC /FIXMBR {enter}
BOOTREC /FIXBOOT{enter}
BOOTREC /SCANOS {enter}
BOOTREC /REBUILDBCD {enter}
Method 3
If it’s not successful or you receive No operating system found or Element not found messages, use diskpart and enter these commands:
DISKPART {enter}
LIST DISK {enter}
SELECT DISK N {enter}
LIST PARTITION {enter}
SELECT PARTITION N {enter}
ACTIVE {enter}
EXIT {enter}
Startup repair – Reboot
If there are still issues, try one more Startup repair and reboot.