“The best theory is inspired by practice.” – Maestro Knuth
Recommended Books (click for Amazon link)
A Self-Learning, Modern Computer Science Curriculum
Introduction
Computer Science is the study of computers and computational systems. Unlike electrical and computer engineers, computer scientists deal mostly with software and software systems; this includes their theory, design, development, and application.
Principal areas of study within Computer Science include artificial intelligence, computer systems and networks, security, database systems, human computer interaction, vision and graphics, numerical analysis, programming languages, software engineering, bioinformatics and theory of computing.
Although knowing how to program is essential to the study of computer science, it is only one element of the field. Computer scientists design and analyze algorithms to solve programs and study the performance of computer hardware and software. The problems that computer scientists encounter range from the abstract — determining what problems can be solved with computers and the complexity of the algorithms that solve them – to the tangible – designing applications that perform well on handheld devices, that are easy to use, and that uphold security measures.
For those that are just starting into programming, I recommend taking a discrete mathematics course, first, then a computer science course, and….then, and only then, select a programming language that interests you (there are numerous languages, and there is no best language). Learn your first programming language at least to an intermediate level, before continuing on to the next language; you’ll thank me later. A great beginner’s language is Python, but I lean towards C#, myself.
Resources
Computer Science Field Guide (University of Canterbury) (website) [free]
Computer Science on reddit (website) [free]
Computer Science on stackoverflow (website) [free]
Computer Science on twitter (website) [free]
Computer Science (Spark Notes) (website) [free]
Teach Yourself Computer Science (website) [free]
Computer Science Research (Cornelll) (peer review) [free]
Computer Science Quizlet (500 sets of cards) (website) [free]
Computer Science 101 (Stanford) (course) [free]
Computer Science Education (OSSU) (course) [free]
CS50’s Introduction to Computer Science (Harvard) (course) [free]
Intro to Computer Science (Udacity) (course) [free]
Introduction to Computer Science and Programming Using Python (MIT) (course) [free]
Tech Dev Guide (Google) (website) [free]
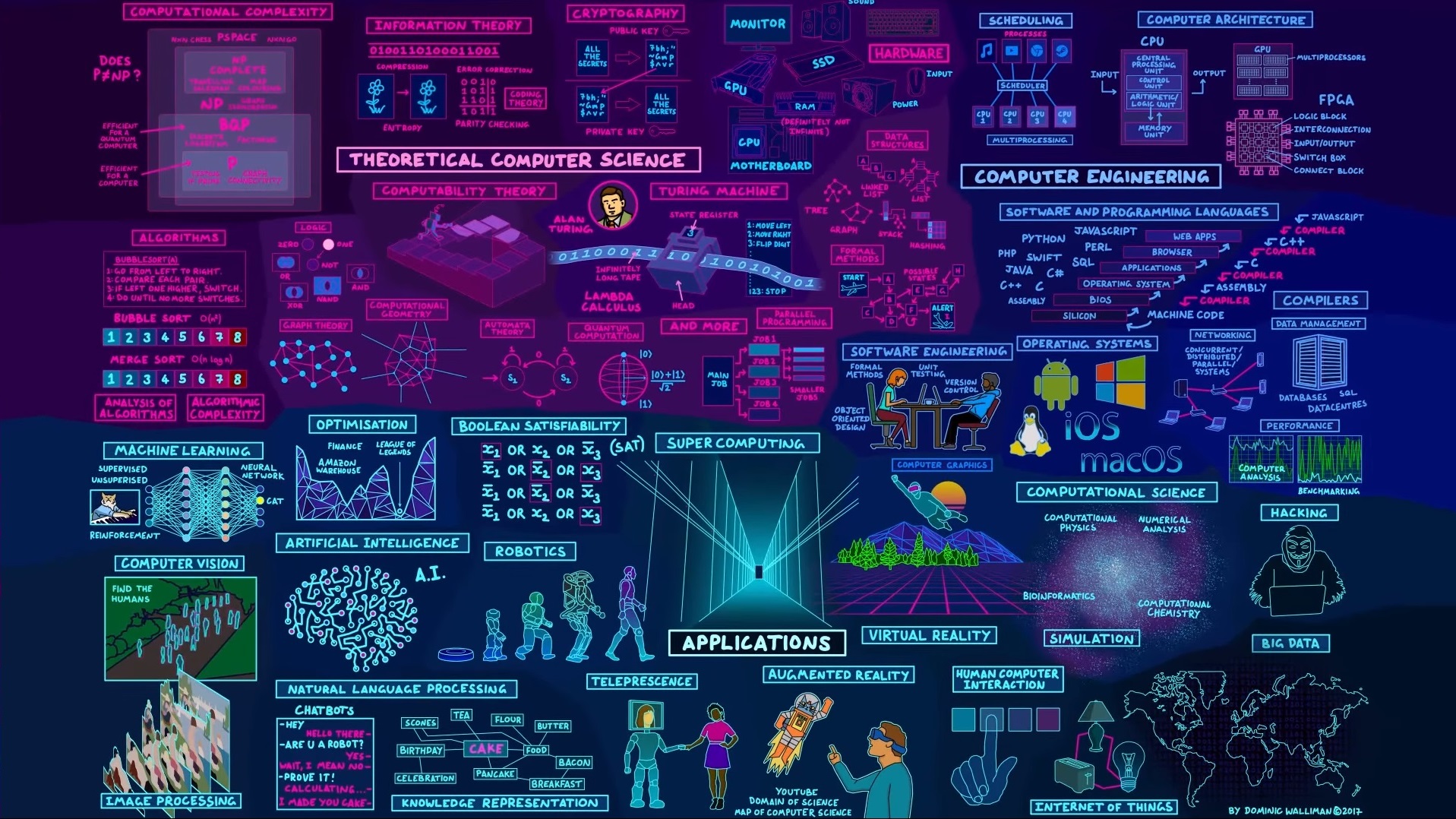
Download CS Wallpaper [free]

The Art of Computer Programming (Amazon) [paid]
* the bible of programming
Seven Big Ideas in Computer Science
Computing is a creative human activity that engenders innovation and promotes exploration.
Creativity and computing are prominent forces in innovation; the innovations enabled by computing have had and will continue to have far-reaching impact. At the same time, computing and computer science facilitate exploration and the creation of knowledge. Computer science emphasizes the creative aspects of computing. Students in computer science will create interesting and relevant artifacts with the tools and techniques of computing and computer science.
Abstraction reduces information and detail to focus on concepts relevant to understanding and solving problems.
People use abstraction every day, but it is a central problem-solving technique in computer science. Traditional examples of abstraction in computer science include control and data abstraction in programming languages as well as analyzing and understanding hardware and software systems. Computer science courses will include examples of abstractions used in modeling the world, in managing complexity, and in communicating with people as well as with machines. Students in computer science will learn to work with multiple levels of abstraction while engaging with computational problems and systems.
Data and information facilitate the creation of knowledge.
Computing enables and empowers new methods of information processing that have led to monumental change across disciplines, from art to business to science. A staggeringly large amount of raw data provides part of the foundation of our information society and economy. People use computers and computation to translate, process, and visualize raw data, creating information. Computation and computer science facilitate and enable a new understanding of data and information that contributes knowledge to the world. Students in computer science will work with data using a variety of tools and techniques to better understand the many ways in which data is transformed into information and knowledge.
Algorithms are tools for developing and expressing solutions to computational problems.
Algorithms help elementary school students learn to multiply, but algorithms realized in software have affected the world in profound and lasting ways. The development, use, and analysis of algorithms is one of the most fundamental aspects of computing. Students in computer science will work with algorithms in many ways: they will develop and express original algorithms, they will implement algorithms in some language, and they will analyze algorithms both analytically and empirically
Programming is a creative process that produces computational artifacts.
Programming and the creation of software have changed our lives. Programming results in the creation of software, but it facilitates the creation of more general computational artifacts including music, images, visualizations, and more. In this course programming will enable exploration and study as well as being the object of study. Computer science will introduce students to the concepts and techniques used in writing programs and to the ways in which programs are developed and used by people; the focus of computer science is not programming per se, but on all aspects of computation. Students in computer science will create programs, translating human intention into computational artifacts.
Digital devices, systems, and the networks that interconnect them enable and foster computational approaches to solving problems.
Digital devices and the Internet have had a profound impact on society. The principles of systems and networks that helped enable the Internet are also critical in the implementation of computational solutions. Computer networks support communication and collaboration. Students in computer science will gain insight into how systems and networks operate, to the principles that facilitate their design, and will analyze the effects of systems and networks on people and society.
Computing enables innovation in other fields including science, social science, humanities, arts, medicine, engineering business.
Computation has changed the way people think, work, live, and play. Our methods for communicating, collaborating, and problem-solving, and doing business have changed and are changing due to innovations enabled by computing. Many innovations in other fields are fostered by advances in computing. Computational approaches lead to new understandings, new discoveries, and new disciplines. Students in computer science will become familiar with the many ways in which computing enables innovation in other fields.
tags: Computer Science, Learn how to program, programming, MrNetTek